ReactiveSearch Pipelines work in a very streamlined manner. However, the execution process might be essential in order to understand how to define pipelines and how to get the best out of them.
This concept guide explains the execution process of pipelines on how the API decides which pipeline should be executed.
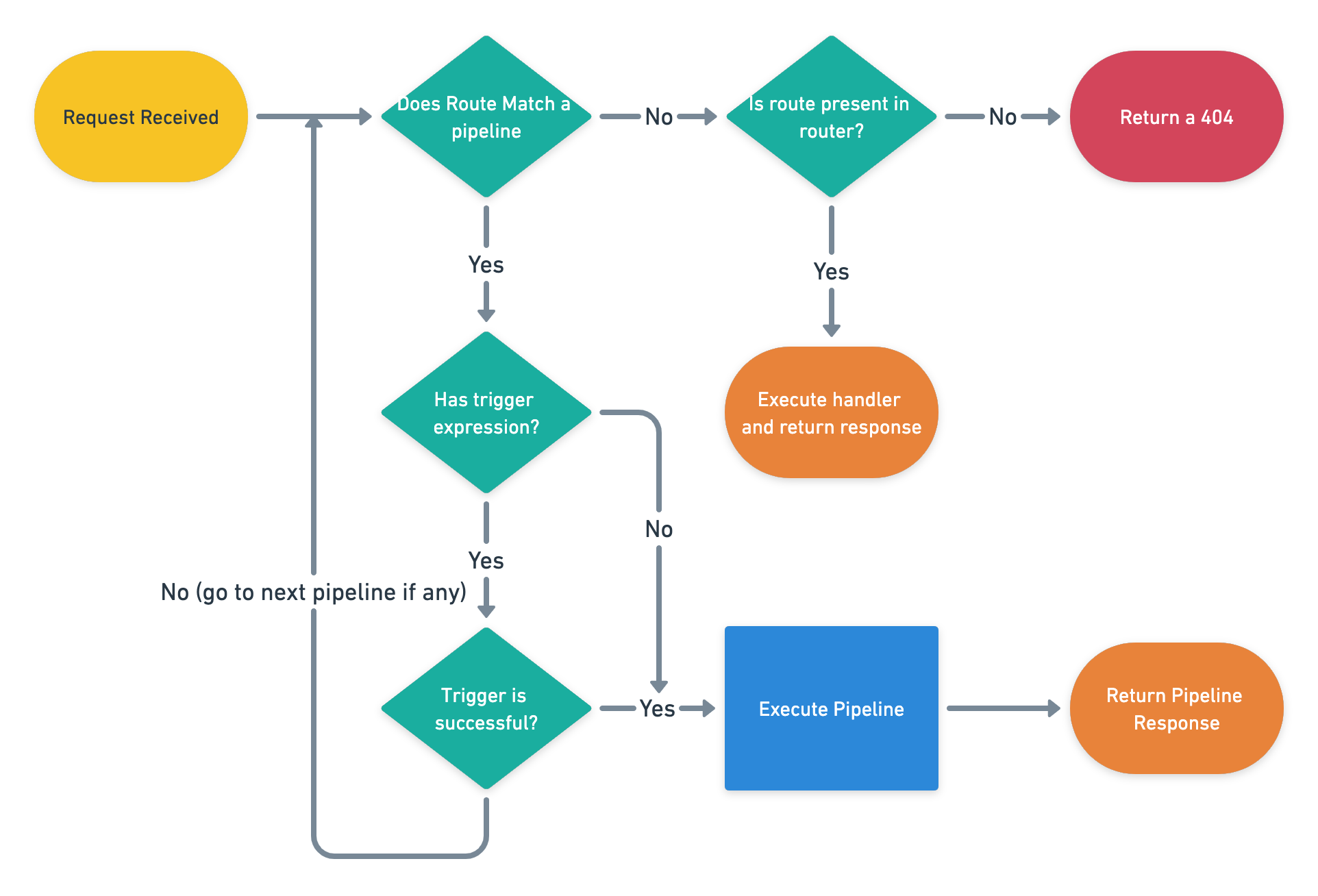
Following whimsical visualizes the execution process of determining which pipeline to execute.
Priority
The routes are iterated in order of priority so the highest priority pipeline route will be present first in the router. This is why the priority field is passed in the pipeline. This lets the developer have control over which pipeline is matched first.
Route Matching
Route matching is done using some complex regex (differs from router to router). This is done by the router and a handler is executed when a route is matched.
Trigger Expressions
Every pipeline route can have a trigger expression. This expression is executed right after the pipeline route is matched. If this expression fails, the execution goes back to the router and tries to match the next present route (keep in mind routes are iterated in order of priority).
Execution Flow
Now that we know how the routes are matched, let's understand how various pipelines are executed. Let's say we have two different pipelines added in our cluster.
- Pipeline 1:
priority 1-> no trigger expression - Pipeline 2:
priority 2-> has a trigger expression
Creating/Updating/Deleting Pipeline
When one of create, update or delete of pipeline happens, the router needs to be shuffled since one of the pipeline routes might have been removed.
What we do in this case is remove the pipeline route from the router altogether. This is because for every pipeline we add each route into the router.
Note that the pipelines are sorted in descending order before they are added to the router. This ensures that the pipelines are executed in the order of priority.
Matcher Function
Now, when a request is received the path of that request is iterated through the routes added (in the order of addition). This happens before the execution goes away from the router level.
It is important to note that the following steps are executed in the router level
Following steps are executed through a Matcher function.
- Route Match?
- Execute trigger (if present) else return
true - If trigger succeeded then return
true - If above failed, return
false
The true and false matters here because the router will pass the execution to the router handler if the matcher function returns true. If the matcher returns false then the router will try to match the next route to the request path.
This gives us the possibility to execute trigger expression before matching that route to that pipeline. So that if the trigger expression fails, the execution can move to another route.



